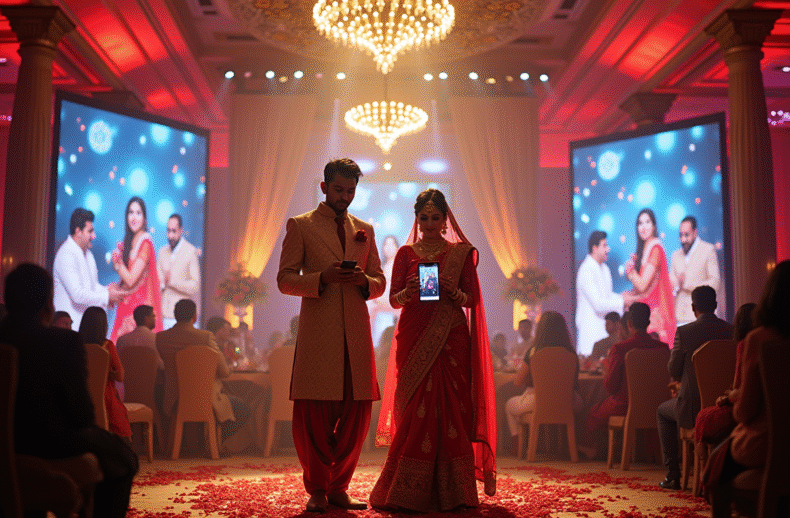
Arranged Marriage, Dating Apps, and the Illusion of Freedom in Modern India In today’s India, the practice of arranged marriage has not vanished—it has evolved. What was once orchestrated by family elders is now curated through digital profiles. Matrimonial sites like Shaadi.com or BharatMatrimony digitize caste, income, complexion, and career into search filters, while dating apps promise autonomy, romance, and…