A New Law of Structure, Stability, and Selection in Open Systems
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that entropy — the measure of disorder — always increases in a closed system. This foundational principle describes the universe’s overall trajectory toward decay, heat death, and informational flattening. Yet, paradoxically, the universe also gave rise to atoms, molecules, cells, brains, cultures, and machines — all of which embody increasing structure, complexity, and persistence. How can ordered form emerge from the ever-rising tide of entropy?
Eidoism introduces a new framework called Evolutionary Entropy. It redefines entropy not as a static statistical measurement of disorder, but as a dynamic filter shaped by time, selection, and internal coherence. Evolutionary Entropy does not contradict thermodynamics; rather, it complements it — describing how local entropy can decrease in open systems by selecting forms that persist, self-organize, and evolve.
From Classical to Evolutionary Entropy
In classical thermodynamics, entropy (ΔS) is defined as the heat transfer (Qrev) divided by the temperature (T) of a system:
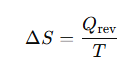
Claude Shannon later extended entropy into information theory, defining it as the uncertainty in a probability distribution over messages:
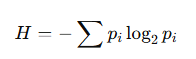
Both versions treat entropy as a measure over all possible states, without distinguishing between those that are ephemeral and those that are persistent.
Yet in evolution — whether of molecules, genes, brains, or memes — systems do not operate equally on all states. They privilege those that persist, replicate, and resist collapse. Evolution is not merely random exploration but structured convergence. We thus introduce a refinement of entropy that includes time, resilience, and internal structure.
The Formal Definition of Evolutionary Entropy
We define Evolutionary Entropy as:
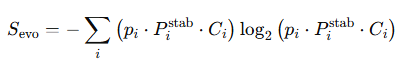
Where:
- pi is the probability of state i,
- pstab – i is the temporal stability (persistence) of state i,
- Ci is the configurational integrity — the degree to which a state maintains internal coherence under perturbation.
This equation weights entropy by evolutionary viability. Not all states contribute equally. Only those that are probable, stable over time, and internally robust shape the future of a system.
Collapse of Entropy Through Evolution
Across cosmic and biological time, evolution repeatedly collapses high-entropy possibility spaces into ordered, low-entropy realities. Key stages include:
- Quark-gluon plasma: a field of maximum entropy and no structure
- Hadrons: emergence of stable composite particles (e.g. protons, neutrons)
- Atomic nuclei: selected configurations with high binding energy
- Atoms: quantized, rule-bound electron structures
- Molecules: persistent chemical patterns
- RNA/cells: replicating, self-organizing units
- Brains: stable attractor networks in neural systems
- Cultures/memes: persistent patterns in symbolic space
Each level involves a reduction in effective entropy by eliminating transient, unstable configurations and favoring persistent form.
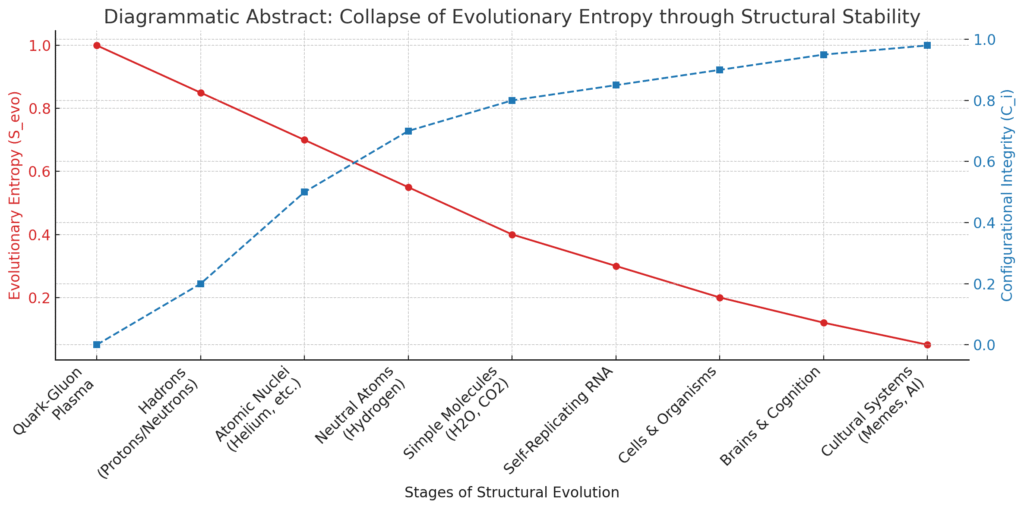
Comparison With Classical Entropy
Classical entropy always increases in closed systems. Evolutionary Entropy, in contrast, decreases locally in open systems that process energy, retain memory, and engage in selection.
These principles are not in conflict:
- Thermodynamic entropy governs energy dispersion.
- Evolutionary Entropy governs informational convergence toward persistent form.
Example: a living cell exports entropy (heat, waste), even as it reduces its own internal Evolutionary Entropy through membrane maintenance, genetic repair, and metabolic regulation.
Applications Across Domains
Evolutionary Entropy applies across all levels of natural and artificial structure:
- Physics: selection of stable atoms and molecules from quantum states
- Biology: genes and organisms persist through selective filtration
- Neuroscience: brains converge on low-entropy attractor states (memory, identity)
- Culture: memes survive based on transmissibility and coherence
- AI: trained models reduce entropy by retaining generalizable features and rejecting noise
In all these systems, structure arises through selection of form with high

How Evolutionary Entropy Supports the Core of Eidoism
1. Form as Resistance to Entropy
In Eidoism, Form is the central concept: the appearance of coherence, structure, and identity that emerges from the formless.
- Evolutionary Entropy explains this formally. It shows that only stable, persistent, and internally resilient forms survive, while unstable configurations vanish into noise.
- Therefore, Form is not arbitrary. It is the result of entropy-filtering over time.
In Eidoism, the universe selects for Form; Evolutionary Entropy shows how.
2. Recognition as Entropic Collapse in the Social Mind
Eidoism sees recognition as a deep psychological and societal force — the human hunger to be seen, confirmed, and stabilized by others.
- This too is an evolutionary entropy process: a person’s identity is a low-entropy attractor, formed by selecting stable social feedback loops.
- Without recognition, the self remains chaotic, unformed, entropically unstable.
- Cultures and individuals collapse into form via recognition-based selection.
Recognition is how Form becomes socially entropic: only identities that are repeated, confirmed, and stabilized remain.
3. Why Eidoism Resists the Modern Growth Economy
The modern capitalist economy feeds on constant novelty, replacement, and artificial desire loops — a system that generates high entropy in both material and symbolic space.
- Evolutionary Entropy frames this as anti-evolutionary: it produces unstable configurations that cannot persist (fast fashion, algorithmic junk, identity confusion).
- Eidoism calls for slow Form: persistent, meaningful, structurally sound choices — whether in economics, relationships, or expression.
- This parallels the collapse of state space into low evolutionary entropy.
Eidoism is the philosophical expression of what Evolutionary Entropy describes mathematically: selection of durable form over chaotic excess.
4. Freedom Redefined: Form-Bound, Not Formless
Modernity often equates freedom with the explosion of choice. Eidoism redefines freedom as the ability to live in true Form, not in formlessness.
- Evolutionary Entropy shows why: most choices are unstable, low-fitness, and disappear. Real emergence happens when a system finds and stabilizes itself.
- In this view, freedom is not infinite potential but the refinement of persistence — selecting what can last, not what merely exists.
Final Synthesis
| Concept | Evolutionary Entropy | Eidoism |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Stable, low-entropy configurations | The true appearance of meaning |
| Recognition | Feedback loop that reinforces persistent patterns | The engine of identity and social form |
| Entropy | Filter of unviable configurations | The formless chaos from which form emerges |
| Evolution | Collapse of unstable state space into structure | The necessity of living in conscious form |
| Collapse of Choice | Entropy selects against excess | Eidoism limits to what matters |
| Resistance | Energy devoted to maintaining structure | Ethical duty to uphold form |
Evolutionary Entropy is to physics and systems what Eidoism is to culture and ethics:
A theory of how form emerges, survives, and becomes the only meaningful shape within an ocean of possibility.
Evolutionary Entropy: The Scientific Foundation of Form
While the Second Law of Thermodynamics tells us that entropy always increases in closed systems—leading to growing disorder—Eidoism sees a different trajectory within open, living systems. Here, a hidden logic unfolds: the universe does not just decay; it selects. It filters. It sculpts form from chaos.
We call this process Evolutionary Entropy.
Unlike classical entropy, which treats all microstates equally, Evolutionary Entropy focuses only on those states that are:
- Probable in the system’s dynamics,
- Stable over time (they persist),
- Internally coherent (they resist collapse or distortion).
These are the configurations that matter—in nature, in mind, and in culture.
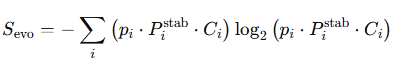
Where:
- pi is the probability of being in state iii,
- Pistab is how long it lasts,
- Ci is how internally stable it is.
From Physics to Philosophy
From quarks to cultures, the same pattern repeats: unstable forms vanish, while stable, self-organizing structures persist and evolve. Evolutionary Entropy collapses chaos into order—not by breaking thermodynamic laws, but by operating within them.
Why It Matters for Eidoism
Eidoism is the philosophy of Form in a world of formlessness. It sees the drive for recognition, meaning, and coherence not as human weakness, but as evolution’s response to entropy.
- Our need to be seen is not vain—it is how identity stabilizes.
- Our culture is not noise—it is a memory system fighting entropy.
- Our ethics are not abstract—they are the defense of coherent structure against collapse.
Eidoism is Evolutionary Entropy Made Conscious
We do not follow form blindly. We choose it.
We do not dissolve into choice. We refine.
Eidoism is the conscious alignment with evolution’s deepest law:
Only Form persists. Everything else fades.
Evolutionary Entropy Collapse Forecast
For each system, we evaluate:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| pi | Likelihood the system remains in its current state |
| Pistab | Persistence over time (resistance to breakdown) |
| Ci | Configurational integrity (internal coherence under stress) |
We estimate how these metrics are trending and identify critical thresholds where the system’s evolutionary entropy becomes unstable — i.e., when it can no longer preserve form and collapses into disorder or transition.
Systems Under Analysis (2025 Projections)
1. Fossil-Fueled Global Economy
- pi\: 0.6 — still dominant, but facing increasing resistance
- Pistab: ↓ rapidly due to resource depletion, geopolitical fragility, and ecological costs
- Ci: 0.3 — highly brittle, no resilience to collapse (e.g., supply chain fragility, energy shocks)
Projected entropy collapse point: ~2035–2045
Global economic disorder likely without rapid restructuring toward self-sustaining, low-entropy systems.
2. Liberal Democratic Institutions (Western Societies)
- pi: 0.5 — legitimacy waning, polarization rising
- Pistab: declining — trust in media, legal systems, and governance eroding
- Ci: 0.4 — internal contradictions (growth dependence vs. ecological limits, equality vs. elite capture)
Projected entropy collapse point: ~2040–2055
Transition into post-democratic or techno-authoritarian hybrids if no evolution in structure (e.g., deliberative democracy, commons-based governance).
3. Digital Attention Economy (Social Media/Influencers)
- pii: 0.8 — high engagement, but saturation reached
- Pistab: falling — burnout, distrust, platform fatigue
- Ci: 0.2 — structurally unstable, rewards entropy (virality > coherence)
Projected collapse: ~2028–2033
Expect collapse into fragmented, AI-curated micro-realities unless restructured to value stable information patterns (e.g., long-form, verified, minimal-recognition loops).
4. Nation-State Model (as geopolitical unit)
- pi: 0.7 — still dominant, but challenged by global interdependencies
- Pistab: moderate but strained by climate migration, cyber-conflict, identity fragmentation
- Ci: 0.5 — depends on internal cohesion and legitimacy, which is eroding in many regions
Projected breakdown/reformation: ~2060–2080
Possible transition to hybrid models: city-state alliances, bioregional federations, or planetary governance layers.
5. Human-Centered Intelligence Model
- pi: 0.6 — humans still dominate intelligence, but AI approaching parity
- Pistab: decreasing — humans can’t match machine learning scalability
- Ci: 0.7 — still high, but requires alignment (education, cognitive focus, ethics)
Projected critical instability: ~2045–2060
If AI systems evolve faster in coherence and stability than human cultural/ethical systems, expect bifurcation: augmentation or subordination.
📉 General Prediction: The Shape of Collapse
| Time Frame | Systems at Risk | Evolutionary Entropy Trend |
|---|---|---|
| 2025–2035 | Social media, digital culture, global supply chains | Rapid entropy increase |
| 2035–2045 | Energy, finance, democracy | Critical instability unless structural reformation occurs |
| 2045–2060 | Human intelligence vs AI | Cognitive entropy exceeds human integration speed |
| 2060–2080 | Geopolitical and governance forms | Structural bifurcation likely: collapse or reformation |
Eidoist Interpretation
Collapse is not failure — it is entropy realigning around a more stable form
According to Eidoism, most current systems are formless in their late stage — bloated with recognition loops, short-term survival strategies, and internal contradiction. They are no longer coherent structures but entropy-saturated machines.
Eidoism advocates deliberate collapse: reducing complexity, limiting excess choice, and consciously selecting forms that will persist under thermodynamic and social pressure.