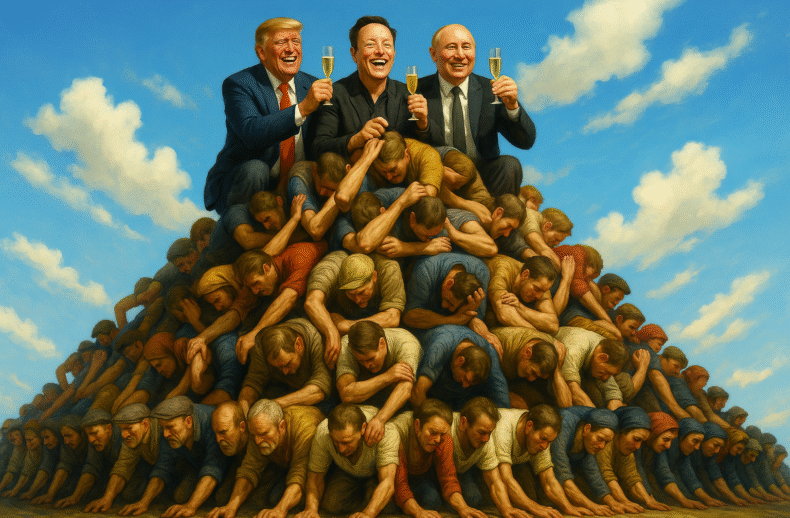
Artificial Intelligence is not a natural force but a man-made disruption. Tech oligarchs dream of production without labor — capital and machines generating wealth without people. To soften the blow, they promote Universal Basic Income, but always leave the question of funding abstract. This is no accident. By framing unemployment as a “social problem” to be solved by government, they privatize profits and socialize losses.
Like CO₂ pollution, AI-driven unemployment is a form of social pollution. The principle must be clear: the polluter pays. If society accepts the oligarchs’ framing, we risk a new feudalism of capital-only production and human irrelevance. If we resist, we can demand an AI dividend: a rightful share of the wealth created by technology, ensuring not only survival but recognition and dignity in a post-labor age.